Glossary of Bandsaw Terms
BAND SPEED
The rate at which the band saw blade moves across the work to be cut. The rate is usually measured in feet per minute (fpm) or meters per minute (mpm).
BASE BAND SPEED
List of recommended speeds for cutting various metals, based on a 4″ wide piece of that stock.
BI-METAL
A high speed steel edge material electron beam welded to a spring steel back. Such a construction provides the best combination of cutting performance and fatigue life.
BLADE WIDTH
The dimension of the band saw blade from tooth tip to blade back.
CARBIDE TIPPED BLADE
Carbide tips welded to a high-strength alloy back, resulting in a longer lasting, smoother cutting blade.
CARBON FLEX BACK
A solid one-piece blade of carbon steel with a soft back and a hardened tooth, providing longer blade life and generally lower cost per cut.
CARBON HARD BACK
A one-piece blade of carbon steel with a hardened back and tooth edge that can take heavier feed pressures, resulting in faster cutting rates and longer life.
CUTTING RATE
The amount of material being removed over a period of time. Measured in square inches per minute.
DEPTH OF PENETRATION
The distance into the material the tooth tip penetrates for each cut.
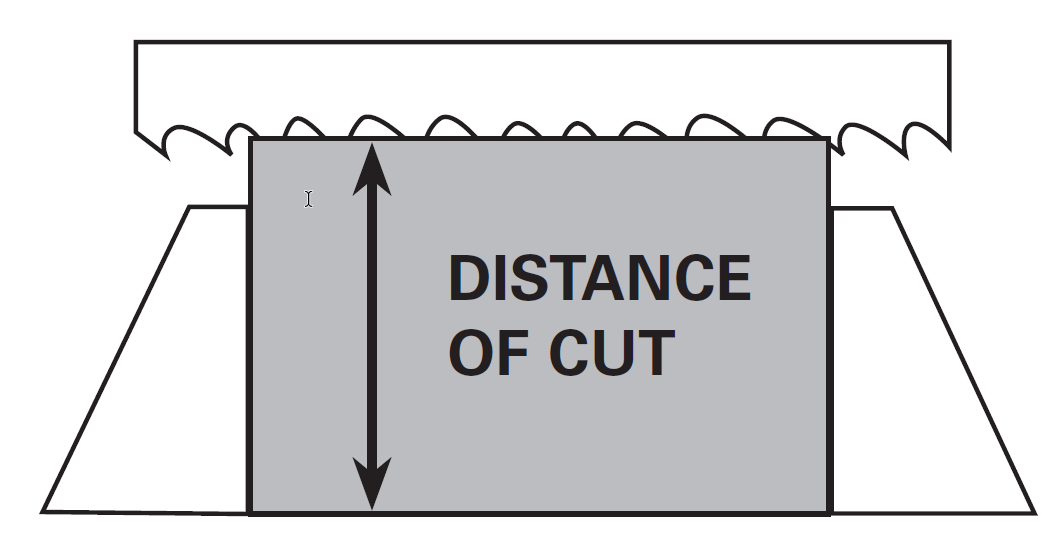
DISTANCE OF CUT
The distance the blade travels from the point it enters the work to the point where the material is completely cut through.
FEED RATE
The average speed (in inches per minute) the saw frame travels while cutting.
FEED TRAVERSE RATE
The speed (in inches per minute) the saw frame travels without cutting.
GULLET
The curved area at the base of the tooth.
GULLET CAPACITY
The amount of chip that can curl up into the gullet area before the smooth curl becomes distorted.
TOOTH FORM
The shape of the tooth, which includes spacing, rake angle, and gullet capacity. Industry terms include variable, variable positive, standard, skip, and hook.
TOOTH PITCH
The distance (in inches) between tooth tips.
TOOTH SET
The pattern in which teeth are offset from the blade. Industry terms include raker, vari-raker, alternate and wavy.
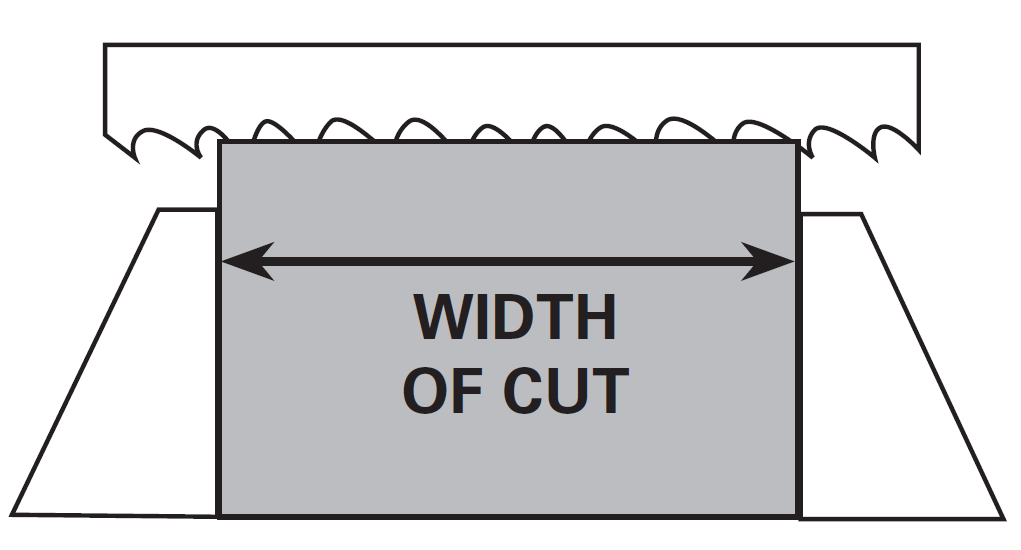
WIDTH OF CUT
The distance the saw tooth travels continuously “across the work.” The point where a tooth enters the work to the point where that same tooth exits the work.